The hair transplant industry is exploding. It’s impossible to ignore. What was once a hush-hush procedure is now a global, multi-billion dollar phenomenon. We see the dramatic before-and-afters, the celebrity endorsements, and the packed clinics in medical tourism hubs.
This has led to a gold rush of doctors, nurses, and technicians all asking the same question: “How do I get a hair transplant training?”
If you’re one of them, you’re probably seeing ads for “2-Day Masterclasses” and “Weekend Certifications.” It all looks so simple. Let’s get one thing straight right now: it’s not.
Hair transplantation is not just a procedure; it’s a craft. It’s a delicate, high-stakes blend of medical science, surgical precision, and raw artistry. You can’t learn it from a PowerPoint. You can’t master it in a weekend.
So, what does real, legitimate hair transplant training actually involve? Who can do it? And what does it cost? Let’s break it all down.
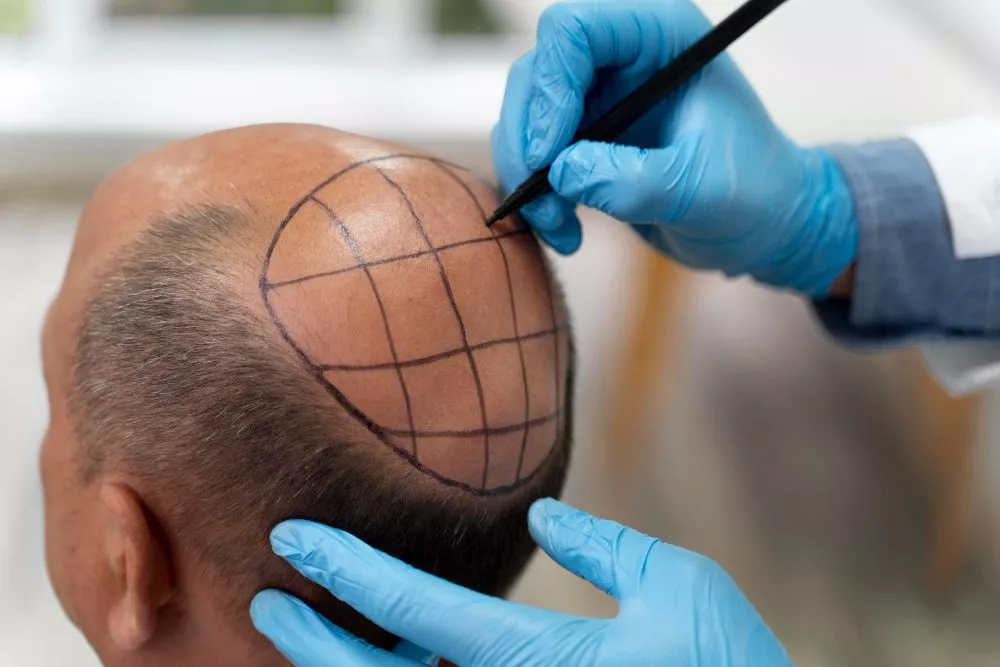
What is Hair Transplant Training?
Hair transplant training is a specialized program that teaches medical professionals how to safely and effectively perform hair restoration procedures. These courses cover key techniques like FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) and DHI (Direct Hair Implantation), combining theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice. Trainees learn patient assessment, donor area management, graft extraction, implantation methods, and post-operative care. Programs are typically led by experienced surgeons and may include live surgeries or simulated sessions.
The training enhances both technical skills and aesthetic judgment required for natural-looking results. Ideal for dermatologists, aesthetic doctors, and surgeons, hair transplant training prepares participants for clinical application and certification. Duration varies from a few days to several weeks depending on course depth.

Career Opportunities After Hair Transplant Training
Hair transplant training opens career opportunities in aesthetic clinics, private practices, and international hair restoration centers. Graduates can work as certified hair transplant technicians or assist in surgical teams under dermatologists and plastic surgeons. Many professionals establish their own clinics, offering FUE, DHI, and scalp micropigmentation services. The growing demand for cosmetic procedures worldwide ensures a steady patient base and financial potential. Medical tourism hubs like Turkey, India, and UAE offer high-paying roles for trained practitioners.
This training also enhances a physician’s portfolio, expanding services in aesthetic and dermatological fields. With proper certification and experience, trainees can pursue global opportunities and long-term career growth in medical aesthetics.

What Will You Learn in Hair Transplant Training?
A good, comprehensive program goes far beyond just “implanting.” It’s an A-to-Z education.
- Patient Assessment and Consultation: This is the most important skill. You’ll learn how to use the Norwood-Hamilton scale, analyze a patient’s hair loss, and—most critically—evaluate their donor area. You’ll learn who is a good candidate, who isn’t, and how to manage their expectations.
- The Art of Hairline Design: This is what separates the masters from the butchers. You’ll learn that a natural hairline is not a straight line. It’s an “irregularly irregular” transition zone. You’ll learn about angles, direction, and flow to create a result that is undetectable.
- Local Anesthesia and Scalp Anatomy: How to safely, effectively, and comfortably numb a patient’s entire scalp for a 6-8 hour procedure. This involves deep knowledge of the scalp’s nerve and blood supply.
- Graft Extraction Techniques (FUE): How to use a manual or motorized punch. You’ll learn how to “feel” for the graft, find the right angle, and extract it without damaging it (transection).
- Graft Handling and Preparation (The Critical Step): This is where many transplants fail. You’ll learn that follicles are living, delicate organs. They must be kept in a specific holding solution (like HypoThermosol or saline) at a specific temperature. You’ll learn to prepare them under a microscope, ensuring they’re not crushed, dehydrated, or out of the body for too long.
- Site Creation and Implantation: This is the “art” part again. You’ll learn how to make the incisions (sites) at the perfect angle and direction to mimic natural hair growth.
- Post-Operative Management: The job isn’t done when the last graft is in. You’ll learn about post-op care, washing protocols, managing swelling, and guiding the patient through the 12-month healing journey.
- Main Techniques Taught in Hair Transplant Training
Your training will center on the modern methods that define the industry.
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): This is the gold standard. Instead of cutting a big strip of skin, you extract follicular units (groups of 1-4 hairs) one by one from the donor area. It’s less invasive, leaves no linear scar, and has a faster recovery. Training is heavily focused on the motor skills of this extraction method.
- DHI (Direct Hair Implantation): This isn’t a different technique so much as a specific method of implantation. After the FUE extraction, DHI uses a tool called a “Choi Implanter Pen.” This pen-like device holds the graft and implants it directly into the scalp in one motion, without the need for pre-made incisions. Training involves learning the specific (and tricky) skill of loading and using this pen.
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): You’ll also learn about the “strip” method. This involves surgically removing a strip of skin from the donor area, and the technicians dissecting it into thousands of grafts under microscopes. While FUE is more popular, FUT is still a vital technique for patients needing a massive number of grafts (megasessions).
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I become certified in hair transplant techniques?
You start by taking a high-quality, hands-on training program to receive a “Certificate of Completion.” This proves you’ve had the training. For physicians seeking the highest credential, the goal is to get “Board Certified” by an organization like the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery (ABHRS), which requires years of experience and passing difficult exams.
Can nurses or non-doctors take hair transplant training?
Yes, absolutely. Nurses (RNs, NPs) and technicians are the backbone of the industry. They take training to become highly-specialized “Hair Transplant Technicians.” Their training focuses on the technical, hands-on skills of extraction, graft prep, and implantation, all of which they perform under the supervision of a licensed surgeon.
What’s the difference between FUE and DHI in training?
It’s simple. FUE is the harvesting method (taking the grafts out one-by-one). DHI is an implantation method (putting the grafts in). When you’re training for “DHI,” you’re almost exclusively learning how to use the “Choi Implanter Pen” to place the grafts. Training for “FUE” can refer to learning the extraction or learning the implantation method of placing grafts into pre-made incisions with forceps.
Is hands-on practice included in all training programs?
If it’s not, it’s not real training. Full stop. You cannot learn this delicate, tactile, surgical skill by watching a video. It’s like learning to play the violin from a book. A legitimate program must include hands-on practice, starting with simulation models and moving to live, supervised cases.
Which countries offer the most reputable hair transplant courses?
This depends on your goal. For sheer volume and mastery of FUE/DHI, Turkey is a global epicenter; the clinics there perform an staggering number of procedures, so their training is based on high-volume experience. For highly-regulated, board-certification-track training for physicians, the USA is the gold standard. South Korea is also renowned for its meticulous, aesthetically-focused training programs.